Bladder cancer is a serious condition that affects the urinary system. Recognizing its symptoms and understanding risk factors can lead to early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Risk Factors for Bladder Cancer
Smoking
Chemical Exposure
Chronic Inflammation
Age
Gender
Family History
Understanding Bladder Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosing bladder cancer involves a series of steps to ensure accuracy. Initially, your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination. If bladder cancer is suspected, they may recommend tests such as urine tests to check for blood or cancer cells, imaging tests like CT scans or ultrasounds to visualize the bladder, and a cystoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder for a closer look. Each of these steps is crucial in forming a complete picture of your health and determining the best course of action.
What is a Cystoscopy?
A simple procedure where a doctor uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera (called a cystoscope) to look inside your bladder and urethra. It helps find problems like tumors, bleeding, or infections
What Tests Are Involved?
Urinalysis – Checks your urine for blood or signs of infection.
Urine Cytology – A lab looks at your urine under a microscope to find cancer cells.
Cystoscopy – A thin tube with a camera is used to look inside your bladder.
Biopsy – During a cystoscopy, the doctor may take a small tissue sample to check for cancer.
Imaging Tests – CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound helps show the bladder and nearby organs to see if cancer has spread.
What Happens After Diagnosis?
Staging and Grading
Doctors find out how far the cancer has spread (stage) and how aggressive it is (grade). This helps decide the best treatment.
Discussing Treatment Options
You’ll meet with your care team to talk about treatments. These may include surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a mix.
Creating a Treatment Plan
A personalized plan is made based on your health, cancer stage, and preferences.
Second Opinions
You can ask another specialist to review your diagnosis and plan if you want reassurance.
Support and Planning
Our team may offer support for nutrition, quitting smoking, mental health, and practical help like scheduling and finances.
Regular Monitoring
Even after treatment starts, you’ll have regular check-ups and tests to watch your progress.
Micro Hematuria vs. Gross Hematuria: What You Need to Know
Micro Hematuria

Micro hematuria refers to the presence of small amounts of blood in the urine, often detectable only through lab tests. While it may not be visible to the naked eye, it can indicate underlying health issues that should be evaluated by a urologist.
Gross Hematuria
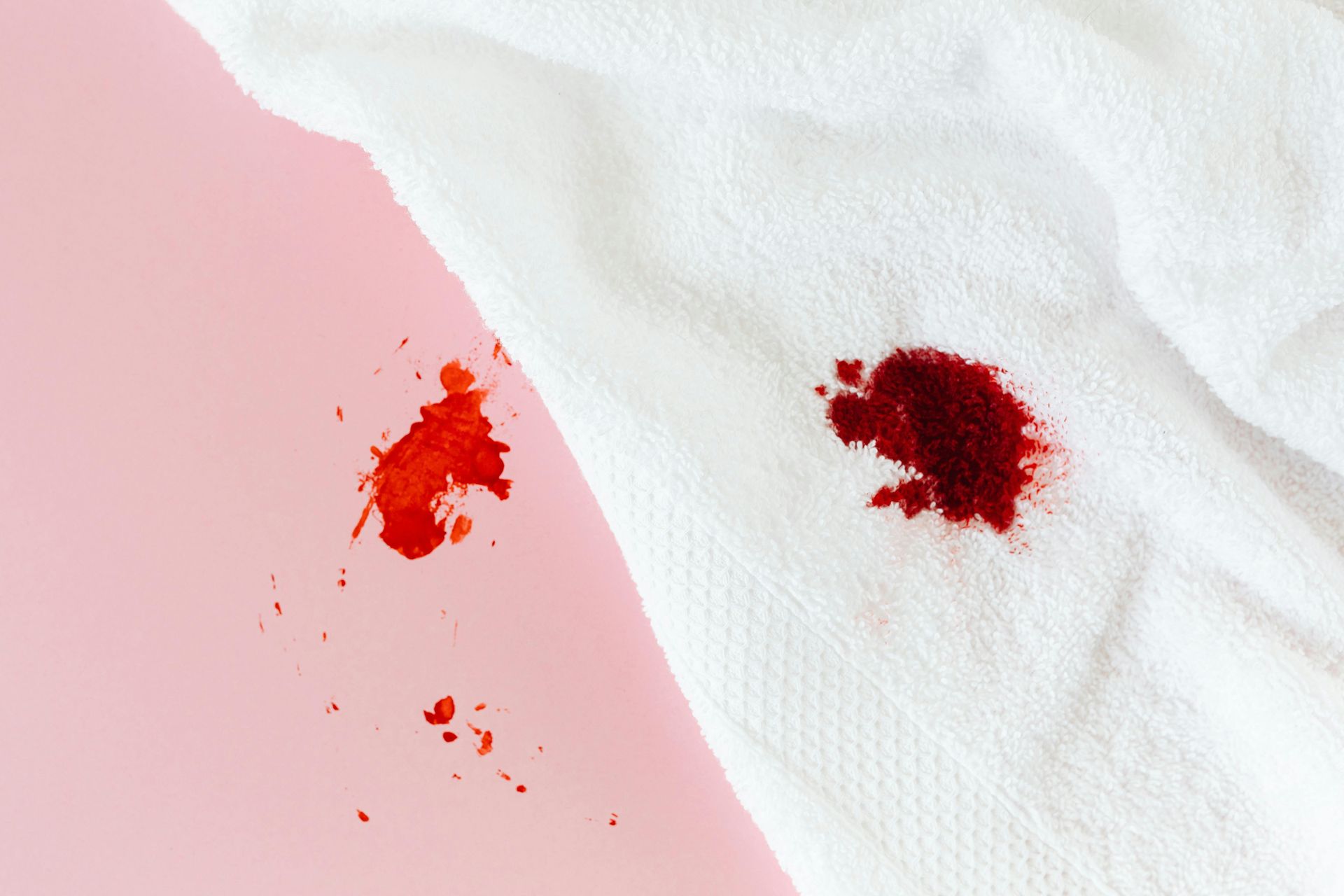

Gross hematuria is characterized by visible blood in the urine. This condition can be alarming and may signal serious health concerns, including bladder cancer. If you notice blood in your urine, it's crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
Exploring New Frontiers in Bladder Cancer Treatment
At The Urology Place, we offer expert bladder cancer care and stay at the forefront of research. Dr. Naveen Kella and our team can check if you're eligible for advanced diagnostic tools or clinical trials as part of ongoing studies.
What Are Clinical Trials?
Why Participate?
Get Expert Guidance on Bladder Cancer
If you or a loved one are facing a bladder cancer diagnosis, don’t go through it alone. Schedule an appointment at The Urology Place for a personalized consultation. Our expert team is here to guide you through your diagnosis, treatment options, and any questions you may have—with care and support every step of the way.